
Perfusion index The perfusion index (PI) derived from a pulse oximeter is calculated as the ratio of the pulsatile blood flow to the non-pulsatile blood in peripheral tissue, 11 and can be measured non-invasively. The uterine artery PI is considered to be increased if it is above the 90th centile. Uterine artery PI provides a measure of uteroplacental perfusion and high PI implies impaired placentation with consequent increased risk of developing preeclampsia, fetal growth restriction, abruption and stillbirth.

Which amino acid has the highest pI value? Amino acid Subsequently, the neutral form arises under conditions of basicity, when the additional -1 charge has been neutralized. The pI of amino acids with acidic side chains In case the side chain is basic, the pI is at a higher pH because the acidic side chain will result in an additional +1 charge. What is the effect of side chains on their pI? The excess OH is attracted to the positively charged amine group resulting in the removal of an H+ ion to form (ce). When pH is greater than pI, there is an excess amount of OH in solution.
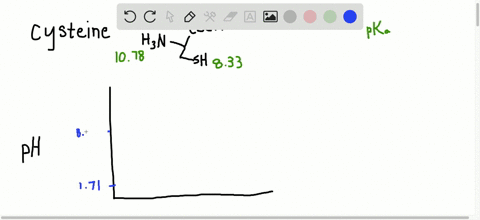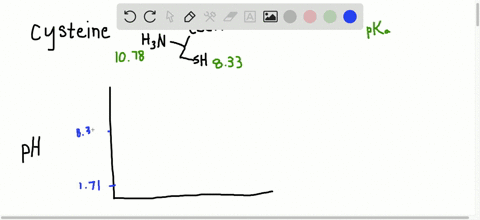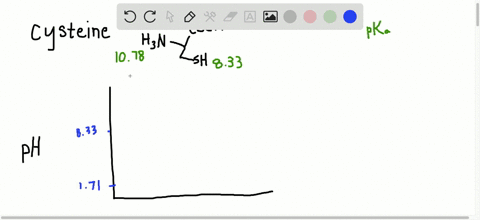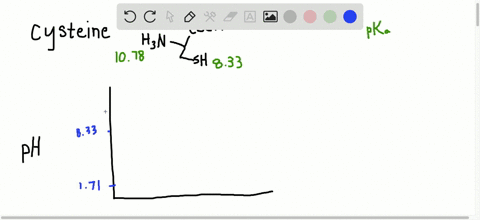
… In decimal form, the value of pi is approximately 3.14. Succinctly, piwhich is written as the Greek letter for p, or is the ratio of the circumference of any circle to the diameter of that circle. Modifications such as phosphorylation that add highly charged groups to the protein can cause easily detectable changes in pI and therefore mobility of the protein in the isoelectric focusing dimension. Read More: How do you make nitrobenzene? What is the average pI of proteins?Īpproximately, 56.44% of the analysed proteins had a pI within the acidic pI range with an average of pI 5.62 (Fig. For a protein with many basic amino acids, the pI will be high, while for an acidic protein the pI will be lower. Isoelectric point (pI): The pH at which the net charge on the protein is zero. Each amino acid has its own pKa (and pI), but can vary according to how many other amino acids are surrounding your target amino acid. PI in organic molecules The pI of a protein is determined by the aggregate pH (and therefore pKa) of every amino acid in the protein chain. What is the pI and how is it determined for a protein? In order to determine the isoelectric point a given protein, we must follow a general rule that consists of two steps (1) Estimate the pH value at which the protein will have a net charge of zero (2) Determine the pKa value right above and right below the estimated pH and find their average. Which amino acid has a greater negative charge at pH 6.20 glycine or methionine?.Why is the side chain pKa so much higher?.How does pH affect net charge of protein?.Why does pH affect the separation of proteins?.How do you calculate the pI of a peptide?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
